We explore the concept of borders in the Episode 106 page of Ramping Up your English. Welcome!

Watching Episode 106
Watch Episode 106 ad-free on archive.org. Click here to watch.
Timeline
A major event during this period was the French and Indian War.


Episode 106 Summary
In this episode, we look at how Native Americans responded to three European powers colonizing North America. By this time in history, we have Spanish, French, and English colonizers changing the ways of life that had been in existence for hundreds of years for various indigenous American groups.
In the English colonies on the East Coast, the pressure of expanding into Native American land caused numerous conflicts, many of them violent. Even in Pennsylvania – established as an example of fair treatment and respect, Native Americans were cheated out of their land.
In Spanish-controlled North America, missionaries had a major role in colonization. Father Kino is remembered as one who respected indigenous ways and formed lasting friendships with Native Americans in the American Southwest. Kino is also remembered as an explorer, mapmaker, rancher, and traveler. Mostly, he is honored as a friend to Southwest tribes like the Pima and the Puma.
Further East, the Caddo people traded with French traders and welcomed Spanish missionaries. Missions were built and missionary word was begun, but an epidemic of smallpox decimated the communities there. When missionaries disrespected Caddo spiritual leaders and said the epidemic was the will of God, they were expelled under threat of death.
For English colonists on the East Coast, the cultivation of tobacco became a major driver of the economy. This only created more pressure on Indian territory and introduced African slaves to this part of North America.
Native Americans allied with the French saw more violence as French and English colonists came in contact with each other. Quebec was attacked and Native Groups in Ohio were encouraged by the French to resist the expansion of Iroquois power into their region. Wars in Europe often resulted in war between allies of French and English interests.
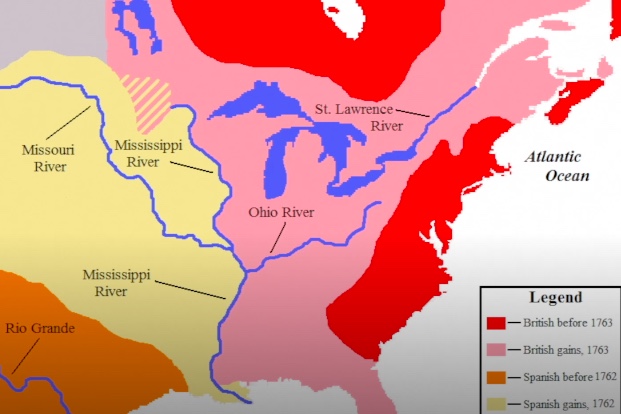
The conflicts eventually resulted in the French and Indian War. Native American allies of the French enjoyed early victories against the English. Forts were built and attacked all along the frontier, with both groups attacking and killing. The English navy proved the deciding factor in the conflict, with the taking of Quebec and later of Montreal. The Treaty of Paris in 1763 ended the war, with France giving up its claim to the expansive New France and Louisiana territories.
The war resulted in France’s exit from North America, leaving French allies at the mercy of the English east of the Mississippi River. While the Spanish presence in the West was little changed by its acquisition of Louisiana – except controlling the Mississippi River from New Orleans – Native Americans east of the river found the English treating them like subjects of conquest.
Language Objectives
Listening Comprehension is the main focus. A great number of events are related in this episode. In watching the video entitled Borders, Viewers strive to relate the major events depicted there. Hence, retelling of the major events is the main objective.
Academic Content Ojectives
Name the main three European countries that made claims in North America.
Name Native American groups who were allies of the French in North America.
Characterize the relationship between French Americans and Native American allies.
Characterize the relationship between English colonies and Native Americans in the same region.
Identify the main conflict between English colonies and Native Americans.
Explain how hunting grounds provided necessities for Native American groups
Trace the development of the English colonies in North America.
Identify the major economic activity in the English colonies..
Characterize the treatment of Native Americans by William Penn and the colony of Pennsylvania.
Explain the role that colonial expansion had on conflict between English colonies and the neighboring Native Americans.
Characterize the deer hide trade and the slave trade in the Southeast.
Explain the connection between the defeat and expulsion of Dutch colonies and the conflict between French and English colonizers.
Explain the significance of the English navy in the French and Indian War
Trace the major events of the French and Indian War.
Characterize the role of Native Americans in the battles of the French and Indian War.
Explain the alliances of some Native American groups with the French and others with the English.
Explain the Proclamation of 1763 and the effect it had on Western Expansion.
Characterize the effects of the 1763 Treaty of Paris on Native Americans and on the colonists in North America.
Based on the outcomes of the French and Indian War, extrapolate the likely future of English influence in North America.
List the main causes of the French and Indian War.
Videos Used in Episode 106
This episode contains a video about this time in history. It’s entitled Borders. Click here to watch the video on ad-free archive.org.
Links to Videos
Along with the images that are generously provided under Creative Commons license, video clips from outside sources helped tell this story in compelling ways. Below are links to the full videos.
The Eastern guard of the Iroquois League was the Mohawk. For a quick history of the Mohawk during European colonization, click here. This You Tube video may have ads.
I’ve always been fascinated by the Caddo People who inhabited part of Louisiana and states to the west. Click here to enjoy a short video about the Caddo.
Compelling audio came from a reenactment of Fort Crown’s Battle. Here’s a link to the reenactment.
Some video came from the reenactment of Braddock’s Defeat. Here’s a link to that Youtube video.
PBS produced a landmark TV program entitled The French and Indian War: The War that Made America. Here’s a link to part one of that production. Click here.
For an alternate production on the French and Indian War, click here.
Click here for a short video about Nouvelle France.
Learn more about Father Kino, the Jesuit missionary who found a middle ground in bringing Christianity to Native Americans in the Southwest. Click here to learn more about him.
A Special Note
The year 2020 brought huge losses to so many people. I hope your family was spared the loss of loved ones, and I pray for comfort if you experienced loss during that difficult year.
One loss that hit close to home was the passing of Thomas Doty, a master traditional Native American storyteller. Doty’s death was not related to COVID19, but it was sudden, and left many friends in shock.
I produced a four-part tribute to Thomas Doty, noting the vital work he’s done to keep some of the Takelma culture and language alive. Links to the four episodes appear below.
Here are the 4 Thomas Doty Tribute programs:https://archive.org/details/pa-aie-102620-doty-tribute-part-1-there-was-ahousehttps://archive.org/details/pa-aie-102920-doty-tribute-part-2-honingthe-arthttps://archive.org/details/pa-aie-110920-doty-tribute-part-3https://archive.org/details/pa-aie-111019-doty-tribute-part-4
Next Episode
Episode 107 looks at the power of uniting. Click here to go to the Episode 107 page.